What is Carbohydrate? What role does it play in human health? And how can we read carbohydrates on food packaging? This article will answer all these questions. Let's explore this nutrient together with Soumaki.
What is Carbohydrate?

Carbohydrate - carbs or saccharides - refers to sugars, starches, and fibers found in plant-based foods and dairy products. Carbs are composed of three elements: C, O, H (carbon, oxygen, hydrogen).
According to Wikipedia, carbs play the following roles:
-
For the human body: storing/transporting energy, preserving muscle, promoting digestive health. Its derivatives also contribute to immune function and fertilization.
-
For biology: participating in the construction of most organic substances on Earth (such as cellulose in plants and chitin in animals...)
In summary, carbohydrate is a primary food source and an essential form of energy for humans and most organisms. Its main role is to transport and store energy.
Classification of Carbohydrate
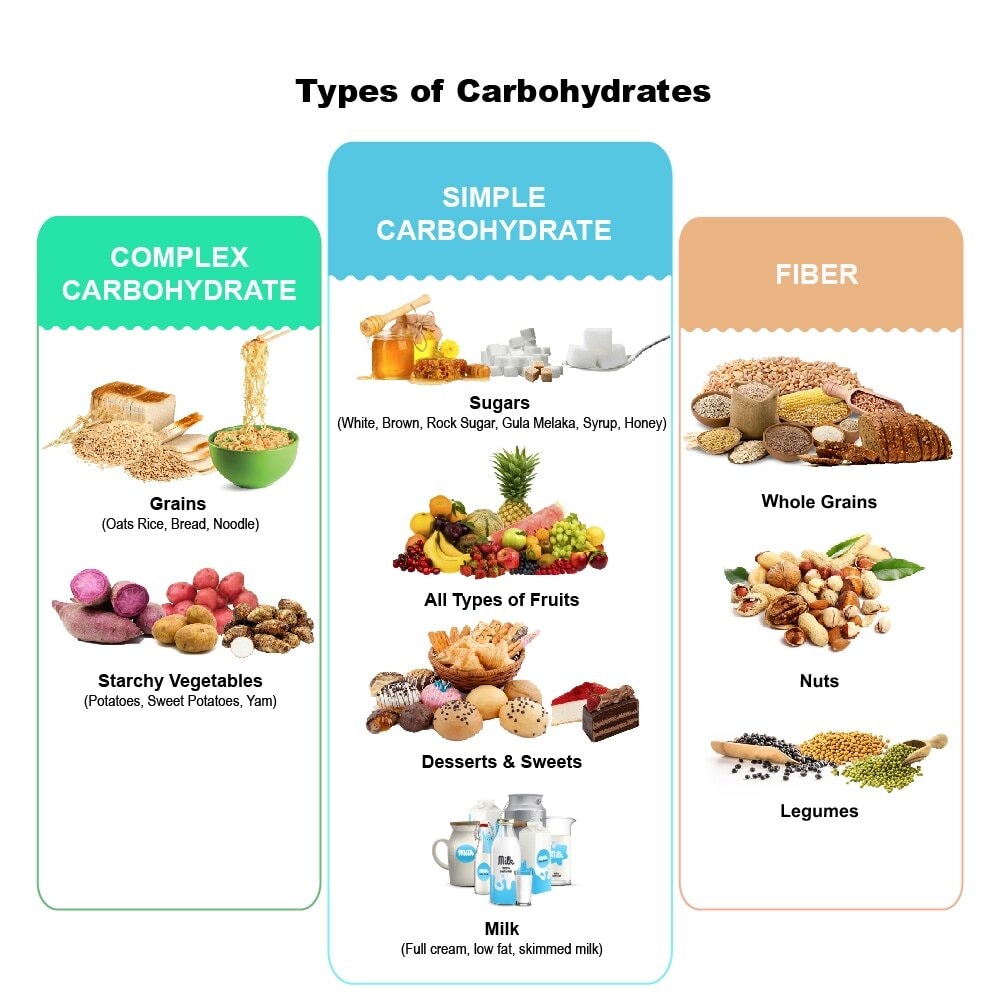
According to NIH, the following types of carbs are found in our daily food:
-
Sugars: also known as simple carbs, these are the most basic form of carb units
-
Starches: also known as complex carbs, are composed of many sugar molecules
-
Fiber: fiber is also a form of complex carb
To help you better understand, Soumaki has created a table comparing and analyzing the two main types of carbs and fiber below:
|
CONTENTS
|
SIMPLE CARBS
|
COMPLEX CARBS
|
FIBER
|
|
Structure
|
Composed of 1-2 sugar molecules (glucose)
|
Composed of 3 or more sugar molecules
|
Similar to complex carbs
|
Common Function
|
Both simple and complex carbs are broken down into glucose (blood sugar) to provide energy for the body.
.
|
Unlike simple/complex carbs, fiber cannot be converted into glucose. Therefore, humans cannot digest fiber
However, bacteria in the digestive system can break down and use the energy provided by fiber
|
Specific Functions
|
Simple carbs are quickly digested by the body, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels
Foods containing simple carbs are high in calories and sodium but low in nutrients, so they are often recommended to be consumed in moderation or limited
|
Complex carbs are digested more slowly, gradually releasing glucose into the bloodstream.
Foods in the complex carb group are low in calories and sodium but high in fiber, so they are often recommended to be consumed more in daily dietary habits.
|
Soluble fiber: can improve stool consistency, support those with constipation, reduce intestinal cramps, prevent cancer, reduce cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Insoluble fiber: can help to prevent digestive and bowel diseases.
|
Foods Source
|
Fructose in fruits
Galactose in milk
Sucrose in table sugar
Maltose in beer, malt candy…
Various types of syrup, raw sugar, and brown sugar.
|
Cellulose in most plant-based foods (grains, vegetables, and fruits)
Chitin in fungi and arthropods (shrimp, crab, shellfish...)
Lignin in meat and the seeds of fruits and grains
Hexose in wheat, barley...
|
Recommended Daily Carb Intake
|
According to FDA guidelines, the average person needs 45-65% of their daily calorie intake to come from carbs (for all age and gender groups). Of that,
a maximum of 10% of calories should come from simple carbs (equivalent to half a candy bar or less than a can of soda with sugar).
For example, if you consume about 2000 calories per day, you need 225-325g of food containing carbs.
|
According to USDA guidelines, the average person needs:
Men
<50 years old: 31-34g per day
> 50 years old: 28g per day
Women
<50 years old: 25-28g per day
>50 years old: 22g per day
|
How to read carbohydrate ingredients on food packaging

Labels on food packaging have nutrition facts, including information about carbohydrates. And here are the notes when reading about this ingredient:
|
CATEGORY
|
NOTE
|
Total carbohydrate
|
Refers to the total weight of sugars, fibers, and other types of carbs in a food product. Note that Total Carbs is different from Net Carbs:
|
|
Dietary fiber
|
Indicates the total amount of fiber in the product
|
Sugars
|
Indicate the total amount of carbohydrates from sugars in the product. Note that sugars can be natural (lactose, fructose) or added (corn syrup, malt syrup...)
|
Sugar alcohols
|
Some products disclose sugar alcohol derivatives below the total carbohydrate amount (such as lactitol, mannitol, maltitol, sorbitol, xylitol…)
Many products labeled "sugar-free" or "reduced calorie" still contain some sugar alcohol derivatives (even though there are other sugar substitutes in the product).
|
|
Other carbohydrates
|
This section indicates the total amount of other types of digestible carbohydrates that are not sugars
|
See also: What are macronutrients?
Questions about foods containing carbs
In this section, Soumaki will answer some common questions from readers:
1. How many carbs should I eat per day?
The amount of carbs each person needs varies depending on their individual needs and body type. However, as previously mentioned, the average daily carb intake for most people is around 45-65% of their daily calorie intake.
2. Which carb-containing foods are good for the body?
-
Vegetables: Almost all types of vegetables are good for the body.
-
Fruits: Apples, bananas, strawberries, grapefruit, cherries, papaya...
-
Beans: green beans, lima beans, lentils...
-
Nuts: almonds, walnuts, peanuts, macadamia nuts, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds...
-
Grains: whole oats, rice, barley, quinoa, millet...
In particular, eating a lot of fiber helps the body feel full, reducing hunger cravings. Leafy greens contain fewer calories than other types of vegetables. If you want to lose weight, leafy greens are a great addition to your daily meals.
3. Do carbs cause obesity?

Yes and no:
-
Yes: added sugars and refined carbs (found in carbonated drinks, fast foods, beer, and wine...) can cause obesity.
-
No: complex carbs and fiber are different: they not only preserve energy and improve health but also help with weight loss and weight management.
In fact, humans have been eating carbs for thousands of years (Asians eat rice and oats, Europeans eat wheat and grains...). So, food from carbs is not bad, only the way of consumption is bad, for example:
-
The Okinawa and Kitavan people have a steady diet of carbs (starch and fiber). They often prepare simple or raw foods. They have the highest life expectancy in the world.
-
Modern Americans in large urban areas often consume a lot of refined carbs and processed foods. Therefore, they are susceptible to obesity, cancer... and negative health outcomes.
Conclusion: Carbs are not the main cause of obesity. When consuming carbs, you need to keep in mind two things:
-
Eat an appropriate amount of carbs for your body type and lifestyle. For example, a person weighing 80 kg and exercising a lot will need to consume more carbs than a person weighing 60 kg and exercising less.
-
Choose the right type of carbs: limit simple carbs and prioritize complex carbs in your diet.
4. How to build a balanced meal with carbs and nutrients?

A nutritious meal is a meal that is full of nutrients, including carbs, protein, and fat. At Soumaki - a healthy restaurant in Saigon, we have designed many meals according to the low-medium-high-calorie needs for customers. At the same time, we also disclose the energy index of the 3 nutrients in each dish, with almost perfect accuracy.
If you need a healthy, quick, and convenient meal, come to 42 Ly Tu Trong, District 1, Ho Chi Minh City, or order through Grabfood to have us deliver delicious, healthy meals to your doorstep.